|
Biomembranes I:
Membrane Structure and Transport
Concept 5: Mechanisms of Active
Transport
Active transport can occur as a
direct result of ATP hydrolysis (ATP pump) or by coupling the
movement of one substance with that of another (symport or
antiport).

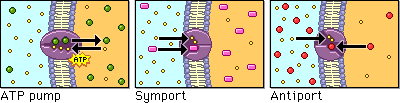
Active transport may move solutes
into the cell or out of the cell, but energy is always used to move
the solute against its concentration gradient.
  |