|
Photosynthesis
Concept 1: An Overview of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
converts light energy into the chemical energy of sugars and other
organic compounds. This process consists of a series of chemical
reactions that require carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) and
store chemical energy in the form of sugar. Light energy from light
drives the reactions. Oxygen (O2) is a byproduct of photosynthesis
and is released into the atmosphere. The following equation
summarizes photosynthesis:
6 CO2 + 6 H2O →
6(CH2O) + 6 O2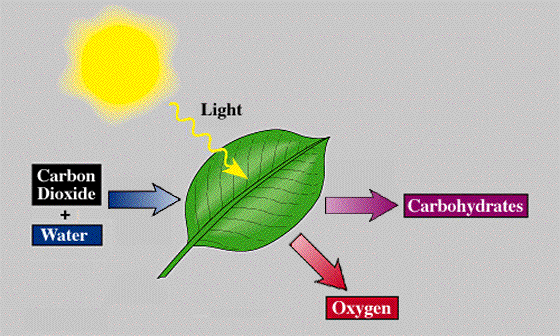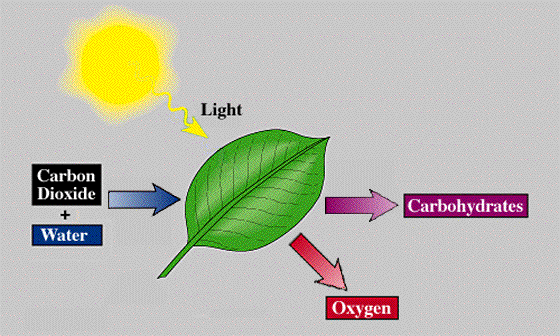
Photosynthesis transfers electrons from water to energy-poor CO2
molecules, forming energy-rich sugar molecules. This electron
transfer is an example of an oxidation-reduction process: the water
is oxidized (loses electrons) and the CO2 is reduced (gains
electrons). Photosynthesis uses light energy to drive the electrons
from water to their more energetic states in the sugar products,
thus converting solar energy into chemical energy.
 |